What Is Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease?

A viral infection known as Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) primarily affects young children under the age of five, while it can also strike older kids and adults [1]. The Coxsackie A virus and the Enterovirus 71 (EV-71) are just two of the viruses that cause the illness [2]. We will talk about HFMD's symptoms, complications, mechanism of transmission and prevention in this article.
The first signs of HFMD are typically a fever and sore throat, which are then followed by tiny, uncomfortable sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside of the mouth [3]. The buttocks, arms, and legs may experience a rash in specific situations [2]. The sickness is typically self-limiting, meaning that it will go away on its own without needing medical attention, and these symptoms typically endure for 7 to 10 days [3].
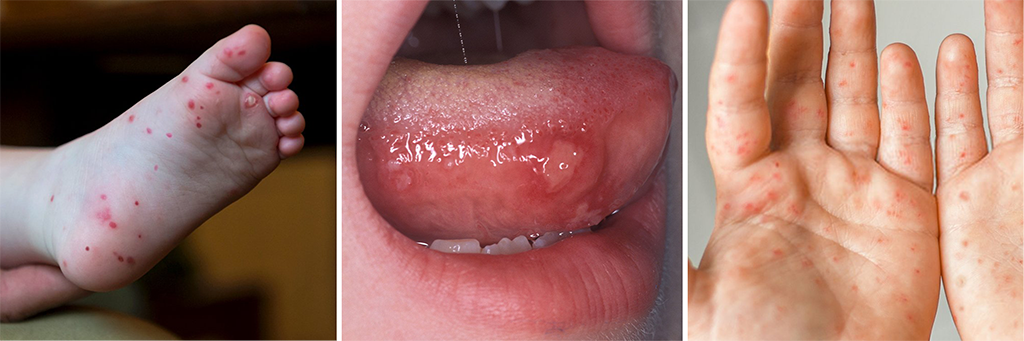
Although HFMD complications are uncommon, the virus can occasionally lead to viral meningitis, encephalitis, or acute flaccid paralysis, which is a sudden loss of muscle tone [2]. Any of these symptoms in a child with HFMD should prompt immediate medical intervention.
Death from HFMD is extremely uncommon and has a very low mortality rate [2]. However EV-71 has been linked to severe HFMD cases, especially in Asia, where outbreaks have happened [1].
HFMD is extremely contagious and is transmitted by coming into contact with an infected person's faeces, saliva, or blister fluid [3]. When an infected individual coughs or sneezes, the virus can potentially spread by respiratory droplets [1]. Those who come into close contact with infected adults as well as kids who attend childcare centres or schools are more likely to get the illness [1].
It is very likely that someone who has been exposed to the virus will acquire HFMD, while not everyone who is exposed will show symptoms [2]. The production of antibodies by the body to combat the virus can aid in infection prevention [1]. Practising excellent hygiene, such as often washing hands and avoiding direct contact with sick people, can also help stop the disease from spreading [2].
The HFMD virus can persist on surfaces for a number of days [3]. Toys, doorknobs, and worktops are a few examples of surfaces that should be cleaned and disinfected since they could be contaminated with the virus.
In summary, HFMD is a viral infection that primarily affects young children, while it can also affect older kids and adults. Fever, a sore throat, and uncomfortable sores or blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth are among the symptoms. Contact with sick people or objects can spread the disease, which is very contagious. Even though complications and fatalities are uncommon, it's crucial to get a child with HFMD immediate help if they exhibit serious symptoms. In order to stop the disease from spreading, it is important to practise good hygiene and clean and disinfect surfaces.
[1] World Health Organization. (2020). Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/hand-foot-and-mouth-disease
[2] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/hand-foot-mouth/index.html
[3] American Academy of Pediatrics. (2018). Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease. Retrieved from https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/infections/Pages/Hand-Foot-and-Mouth-Disease.aspx
Powered by Mirasvit Magento 2 Extensions